Environment Variables
Extension comes with built-in support for environment variables via .env file (and similar).
[!warning] This feature is not stable yet. You can track its development here.
Take for example, our ChatGPT $(Template).
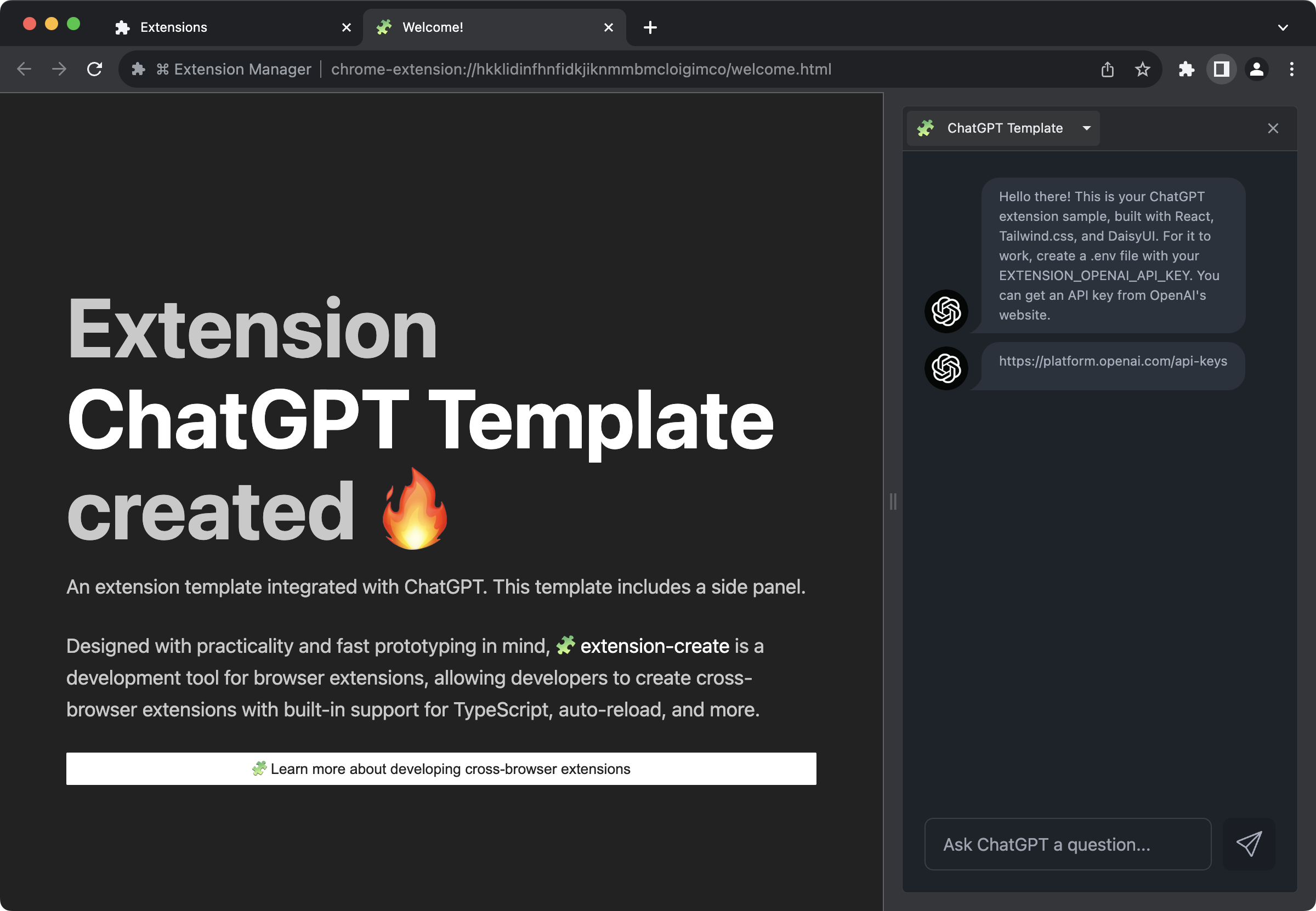
See that it expects the EXTENSION_OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable? Create an .env file at the project root so Extension can parse its contents at runtime.
The following file names are supported:
.env.env.local.env.defaults.env.example
How To Use
- Create a new file using one of the supported file names at the same folder level as your
manifest.jsonfile. - In your extension code, add the Node.js pattern of
process.env.YOUR_VARIABLE_NAME.
TIP: Environment variables are not supported in the
manifest.jsonfile.
See the sample below:
Will output the following:
ON THIS PAGE